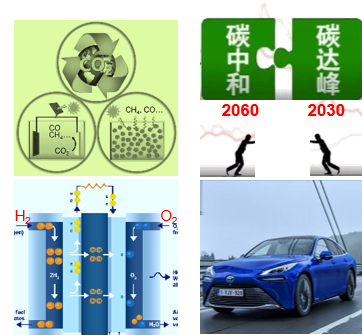
1) Electrochemical reduction of CO2 has a potential of becoming a major contributor to sustainable production of fuels and chemicals such as ethylene or ethanol using abundant renewable electricity, while the sluggish CO2 reduction kinetics as well as complex electrons coupled protons transfer process render the CO2 valorisation process challenging.
2) Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) with high efficiency and nonpollution characteristics have attracted massive attention from both academic and industrial communities due to their irreplaceable roles in building the future sustainable energy system.